What Is Car Window Trim Moulding? A Complete Guide for Automotive Parts Buyers and Engineers
Introduction
Why Car Window Trim Moulding Matters
Car window trim moulding plays an outsized role in the look, feel, and performance of every modern vehicle. Far beyond mere decoration, this precision-moulded profile seals the glass-to-body interface against wind, rain, and road noise—and is often one of the first visual cues of a vehicle’s overall quality. OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers rely on advanced car window trim moulding to meet stringent standards for fit, finish, and durability.
-
Seal & Protect: Prevents water ingress and shields cabin acoustics from wind noise.
-
Elevate Aesthetics: Chrome, gloss-black, or matte finishes add visual flair and brand identity.
-
Ensure Safety: Guards the glass edge from chipping and distributes impact loads in minor collisions.
In this guide we’ll explore:
-
What Is Car Window Trim Moulding?—Definition, function, and common profiles
-
Common Materials Used—TPU, TPE/TPV, PVC, ABS+PC, and more
-
How Car Window Trim Mouldings Are Manufactured—Injection vs. extrusion, mould design essentials
-
Applications in Different Vehicle Types—Sedans, SUVs, trucks, and EVs
-
Key Considerations for Buyers and Engineers—Material selection, mould lifespan, supplier vetting
By diving deep into each area, you’ll gain the knowledge needed to specify, source, or manufacture best-in-class car window trim moulding for any automotive program.
What Is Car Window Trim Moulding?

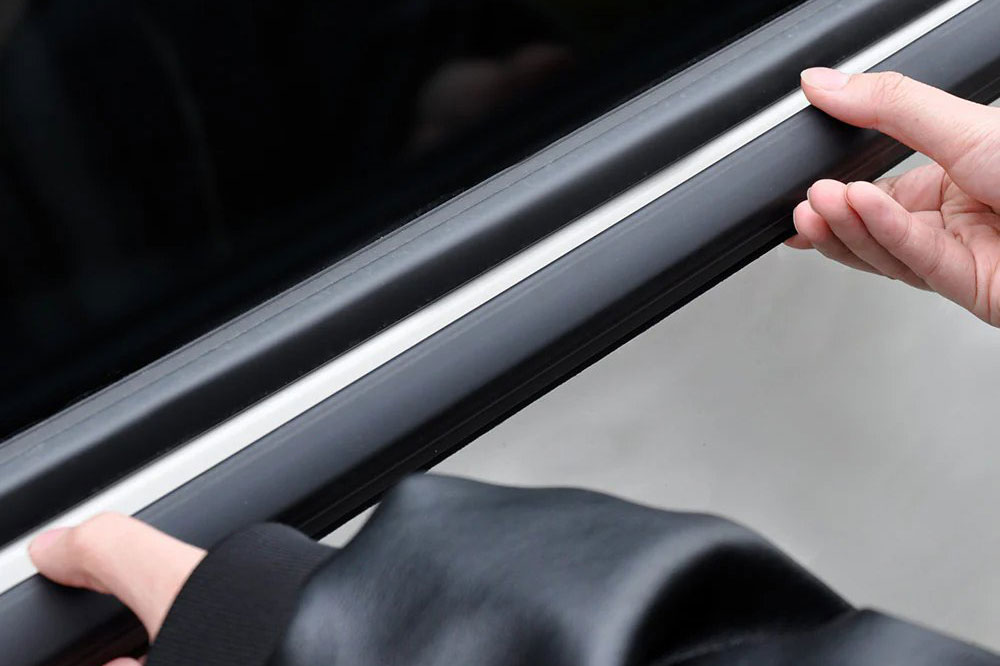
Definition and Core Function
Car window trim moulding refers to the injection- or extrusion-moulded plastic profiles that run along the perimeter of automotive glass. These trims fit into dedicated channels in the door frame or window aperture. Their primary roles are:
-
Aesthetic Framing: Providing a clean, finished boundary around the glass, often accentuated with metallic or high-gloss coatings.
-
Weather Sealing: Blocking rain, dust, and wind—critical for passenger comfort and preventing corrosion.
-
Noise Reduction: Acting as a barrier to wind buffeting and external road noise, enhancing cabin quietness.
-
Edge Protection: Shielding the glass edge from chipping or abrasion during operation.
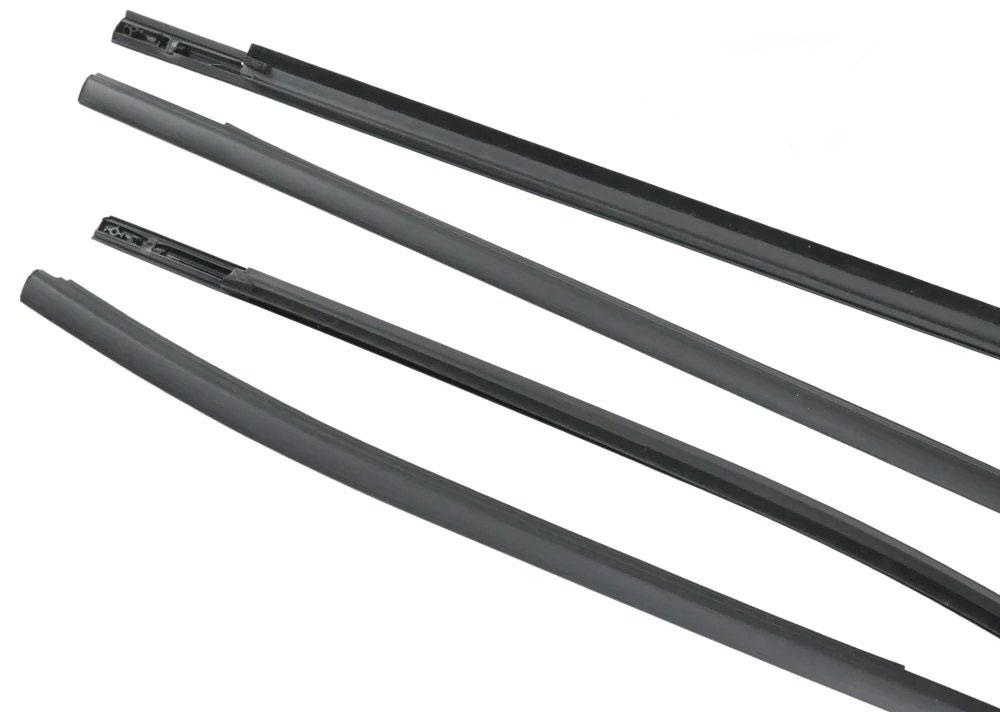
Common Trim Profiles
Modern vehicles may employ several trim styles, each requiring specific mould designs:
-
Beltline Moulding: Runs horizontally along the lower edge of side windows, often chrome-plated.
-
Pillar Seals: Vertical trims that cover door pillars, providing a continuous visual line.
-
Gasket Seals: Soft, rubber-like profiles that press directly against the glass for airtight sealing.
-
Gutter Mouldings: Channel rainwater away from doors via integrated scuppers.
Design Parameters
Achieving consistent fit and finish demands tight tolerances—often ±0.05 mm. Mould cavities must account for:
-
Variable Wall Sections: To manage flow and cooling of different cross-sections without sink marks.
-
Under-cuts & Snap Features: For secure retention in the body’s window channel without adhesives.
-
Surface Textures: From polished cavities for glossy trims to patterned ones for matte finishes.
With such exacting requirements, car window trim moulding moulds are among the most complex tooling in automotive plastics.
Relevant Standards:
- ISO 2768(General Tolerance Standard)
- DIN 7168(Machining Dimensional Tolerances)
- GB/T 1804(Chinese Dimensional Tolerance Standard)
Common Materials Used in Window Trim Moulding
Selecting the right car window trim moulding material is pivotal for balancing cost, durability, aesthetics, and environmental resistance. Below are the top materials and how each influences part performance.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
-
Key Traits: High abrasion and tear resistance, excellent elasticity (Shore 60–95A).
-
Benefits:
-
Superior scratch resistance—retains gloss even after repeated door use.
-
Wide hardness range for tailored “soft-touch” seals.
-
Good UV and ozone resistance—long outdoor life.
-
-
Applications: Luxury vehicles with high-gloss, color-matched window surrounds.
-
Processing Considerations: Requires precise drying (moisture <0.05%) and controlled melt temperatures (180–230 °C).
TPE / TPV (Thermoplastic Elastomers / Vulcanizates)
-
Key Traits: Rubber-like flex, recyclable, broad service temp (–40 to 120 °C).
-
Benefits:
-
Environmentally friendly (often free of PVC).
-
Excellent weatherability and color stability.
-
Simplified injection moulding—no secondary vulcanization.
-
-
Applications: Mid-range cars, interior window seals, flexible edge guards.
-
Processing Considerations:
-
Lower melt temperatures (180–220 °C).
-
Can be over-moulded onto rigid substrates in two-shot processes.
-
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
-
Key Traits: Rigid or flexible grades, very low material cost.
-
Benefits:
-
Easy to compound for desired hardness (Shore A 60–90).
-
Good dimensional stability and chemical resistance.
-
Economical for high-volume trims on mass-market models.
-
-
Applications: Budget vehicles, non-critical exterior mouldings.
-
Considerations:
-
Environmental concerns over plasticizers—must use phthalate-free grades.
-
Requires careful control of processing to avoid degradation (PVC dehydrochlorination above 200 °C).
-
ABS + PC Blends
-
Key Traits: Combines ABS’s processability with PC’s toughness.
-
Benefits:
-
High heat deflection (>100 °C) for body shop durability.
-
Excellent surface gloss and paint adhesion.
-
Superior impact resistance compared to pure ABS.
-
-
Applications: Structural trims requiring rigidity, e.g., fixed rain gutters.
-
Processing Considerations:
-
Higher mould temperature (80–100 °C).
-
Drying required (0.02% moisture) to avoid voids.
-
Additional Specialty Materials
-
EPDM Rubber: For ultra-soft seals on premium SUVs—offering extreme cold flexibility (–50 °C).
-
Nylon (PA6/PA66): In high-stress hinge covers where mechanical durability is paramount.
-
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate): UV-stable alternative to ABS for sustained outdoor gloss.
Material Impact on Performance & Cost
| Material | Durability | Appearance | Cost | Recyclability | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPU | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | High | Moderate | Luxury window seals, soft grips |
| TPE / TPV | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | Medium | High | Interior seals, flexible trims |
| PVC | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | Low | Low | Economy models, simple extrusions |
| ABS+PC | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | High | Moderate | Structural gutter mouldings |
| EPDM / Nylon / ASA | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | Varied | Varied | Specialty seals, hinge covers |
How Car Window Trim Mouldings Are Manufactured
The manufacturing of car window trim moulding demands strict control over every process step to ensure perfect fit, finish, and function.
4.1 Injection Moulding Process
-
Mould Design & Simulation
-
CAD modelling of the cavity with uniform wall thickness.
-
Moldflow analysis to balance fill, minimize weld lines, and predict shrinkage.
-
-
Tooling Fabrication
-
Hardened steel (P20, 1.1730) for high-volume production; aluminum prototypes for low-volume or testing.
-
Precision EDM to achieve surface finishes of Ra 0.2 μm for gloss trims.
-
-
Injection & Cooling
-
Melt temperatures tailored to material (e.g., TPU at 200 °C, PVC at 180 °C).
-
Conformal cooling channels for uniform solidification, reducing cycle by up to 30%.
-
-
Ejection & Secondary Operations
-
Controlled ejection pin placement to avoid part deformation.
-
Post-mould trimming or in-mould assembly for inserts (e.g., metallic accents).
-
4.2 Extrusion Moulding Process
-
Continuous Profile Production: Melting resin in a screw barrel → pushing through a precision die → calibration via vacuum sizing → cooling in water troughs → cutting to length.
-
Advantages: Cost-effective for long runs of simple cross-sections; seamless joints available via butt welding.
-
Limitations: Less adaptable to complex shapes and finishes compared to injection moulding.
4.3 Mould Structure Requirements
-
Runner & Gate Design: Hot-runner systems to eliminate waste for high-value materials like TPU.
-
Draft Angles: Minimum 1–3° draft to ensure easy ejection without damaging fine features.
-
Surface Texture: Custom laser-etched textures for patterned finishes—matte or leather-grain effects.
-
Ventilation: Micro-vents at mold parting lines to avoid burn marks and air traps.
4.4 Quality Assurance
-
In-process Monitoring: Pressure and temperature sensors in the mould to detect fill anomalies.
-
First-Off Inspection: CMM measurement of trim profile against CAD data, ensuring +/-0.05 mm tolerance.
-
End-of-Line Checks: Go/no-go gauges for snap-fit features, visual inspection of surface finish and color match.
Applications in Different Vehicle Types
5.1 Sedans & Hatchbacks
-
Trim Style: Slim chrome or painted inserts providing elegant visual lines.
-
Material Choice: ABS+PC for high-gloss paintability and dimensional stability.
-
Performance Needs: Moderate weather sealing; focus on refined styling.
5.2 SUVs & Crossovers
-
Trim Style: Rugged TPE/TPV seals with UV-resistant coatings.
-
Material Choice: TPE blends for flexibility and durability in off-road environments.
-
Performance Needs: Enhanced dust and splash protection; wide temperature range stability.
5.3 Trucks & Commercial Vehicles
-
Trim Style: Durable EPDM or nylon gaskets for heavy-use conditions.
-
Material Choice: EPDM for its excellent low-temperature flexibility and abrasion resistance.
-
Performance Needs: Long service intervals; chemical resistance to fuels and cleaners.
5.4 Electric Vehicles (EVs)
-
Trim Style: Lightweight TPU or ASA trims matching sleek, modern aesthetics.
-
Material Choice: TPU for optimal balance of weight, durability, and high-gloss finish.
-
Performance Needs: Minimal weight addition to maximize range; high UV stability for rooftop glass.
Key Considerations for Buyers and Engineers
When specifying car window trim moulding, buyers and engineers must weigh multiple factors to ensure the chosen solution aligns with performance, budget, and production requirements.
6.1 Material Selection Guidelines
-
Weather Resistance: UV, ozone, and temperature cycling tests for outdoor trims.
-
Mechanical Properties: Shore hardness (A60–95) vs. tensile strength for impact protection.
-
Cost vs. Value: Balance material cost with expected part lifespan and warranty requirements.
6.2 Mould Lifespan & Volume Matching
-
Prototype / Low Volume: Aluminum tooling (5,000–50,000 cycles) for design validation.
-
Production / High Volume: Hardened steel tooling (≥1 million cycles) amortized over large runs.
6.3 Tolerance & Fitment Requirements
-
Dimensional Control: Critical for snap-fit features; specified as ±0.05 mm or better.
-
Surface Spec: Gloss grade, texture patterns, and color consistency across batches.
6.4 Supplier Selection Criteria
-
Automotive Credentials: IATF 16949 certification, track record with OEM programs.
-
Technical Capability: In-house toolmaking, CAD/CAM, flow simulation, and rapid prototyping.
-
Delivery & Support: Predictable lead times, local/regional stocking, dedicated technical service.
Why Choose Huazhi?
-
15+ years of expertise in automotive mould manufacturing
-
State-of-the-art CAD/CAM, flow simulation, and rapid prototyping
-
IATF 16949 certified quality management
-
Full turnkey service: tooling design → production → post-mould finishing
Conclusion
Car window trim moulding is a small component with a big impact—blending style, function, and protection. By selecting the right materials (TPU, TPE/TPV, PVC, ABS+PC) and leveraging precise injection/extrusion moulding, automotive manufacturers ensure superior fit, finish, and long-term performance.
🚘 Ready to elevate your vehicle’s trim quality?
📞 Contact Huazhi today for a free material consultation, custom mould quote, and expert support on your next car window trim moulding project!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the typical lead time for producing a car window trim moulding tool?
A1: Prototype aluminium tools: 4–6 weeks. Production steel tools: 10–14 weeks, depending on complexity.
Q2: Can we produce two-shot or over-moulded window trim mouldings?
A2: Yes—Huazhi offers two-shot injection moulding and insert over-moulding to combine rigid and soft materials seamlessly.
Q3: Are these trim materials recyclable?
A3: Most TPU, TPE/TPV, ABS+PC, and ASA grades are recyclable under proper automotive recycling programs. PVC is less recyclable due to plasticizers.
Q4: Do you provide custom OEM mould design & development?
A4: Absolutely. From DFM consultation to prototyping, full-scale tooling, and part qualification, we deliver turnkey OEM/ODM mould solutions.